
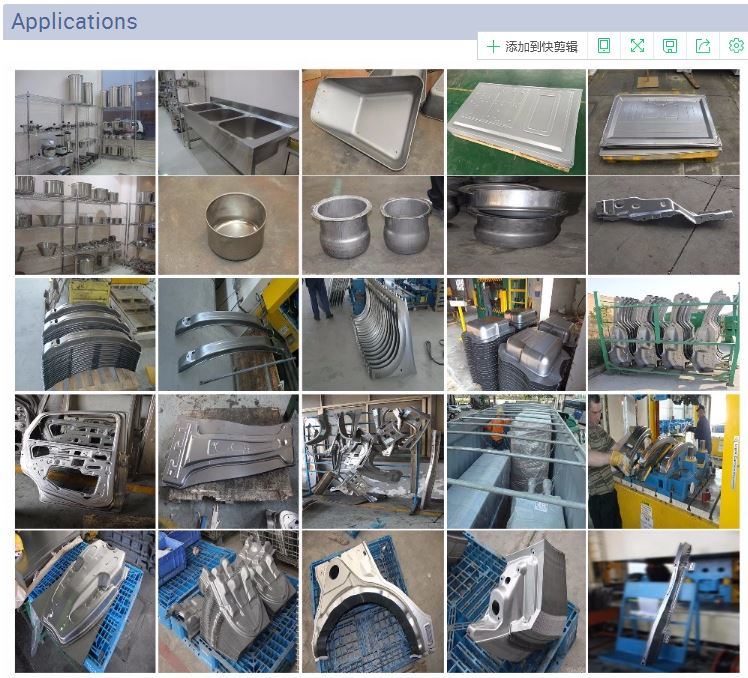
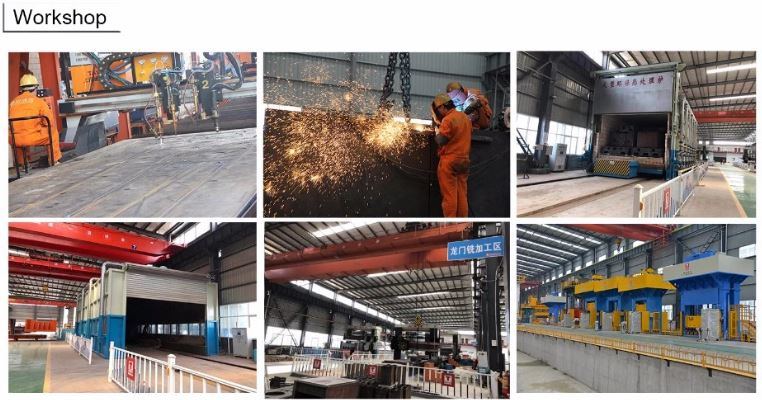
Creating a stainless steel product from scratch is a complex process that involves advanced technology, precise engineering, and deep scientific knowledge. While stainless steel is widely used in everyday life, few people understand the detailed steps involved in its production. The manufacturing of stainless steel is not only fascinating but also highlights the significant progress made in material science over the years. Here are six essential stages in the stainless steel manufacturing process:
1) Material Handling
Uncoiler: This machine is placed at the beginning of the production line and is responsible for holding and unrolling the steel strip safely. It regulates the speed and direction of the metal as it unwinds from the coil and moves to the next stage of processing, such as slitting or entering a tube mill.
2) Forming
Deep Drawing Press: In this phase, semi-finished steel shapes undergo various forming operations. For example, stainless steel may be hot rolled—meaning it is heated and passed through large rolls. Blooms and billets are transformed into bars and wires, while slabs are formed into plates, strips, or sheets. Bars are particularly versatile due to their wide range of grades and sizes, suitable for different applications like round, square, octagonal, or hexagonal shapes.
3) Heat Treatment
Annealing Furnaces: During heat treatment, stainless steel is subjected to controlled heating and cooling to relieve internal stresses and improve material properties. This step ensures the metal becomes more malleable and suitable for various applications. Precise control of temperature, pressure, and cooling rate is crucial to avoid defects.
4) Descaling
Pickling: After annealing, scale forms on the surface of the stainless steel. This layer is removed using processes collectively known as descaling. Pickling is one of the most common methods, involving chemical treatments to clean the surface and prepare it for further processing.
5) Cutting and Punching
In this stage, the semi-finished, heat-treated, and descaled stainless steel is cut into specific shapes. Mechanical cutting techniques include guillotine knives, blanking, nibbling, and high-speed blades. Additionally, features such as tap holes and overflow channels are created during this step.
6) Finishing and Polishing
Polishing Machine: This final step enhances the aesthetic appeal of the stainless steel product. Finishes are applied to make the surface smooth, easy to clean, and suitable for sanitary environments. Polishing also improves the durability and visual quality of the finished item.
Hydraulic Press 4 Column Hydraulic Sheet Metal Deep Drawing
Features:
1. A hydraulic machine that uses hydrostatic pressure to process materials such as metal, plastic, rubber, wood, and powder.
2. Widely used in pressing, forming, forging, stamping, cold extrusion, bending, flanging, sheet metal deep drawing, powder metallurgy, and press-fit operations.
3. Offers technical and economic advantages by reducing weight, minimizing the number of parts and molds, improving stiffness and strength, and lowering production costs.
SPECS of Yz33
| Model | Unit | Yz33-25T | Yz33-50T | Yz33-63T | Yz33-100T | Yz33-160T | Yz33-250T | |
| Clamping Force | KN | 250 | 500 | 630 | 1000 | 1600 | 2500 | |
| Working Layer | Qty | 2~4 | 2~4 | 2~4 | 2~4 | 2~4 | 2~4 | |
| Piston Stroke | mm | 180 | 250 | 250 | 250/250 | 250/250 | 500 | |
| Heating Platen Daylight | mm | 90 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | |
| Heating Platen Size | Left-right | mm | 350 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 750 | 900 |
| Front-back | mm | 350 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 850 | 900 | |
| Heating Plate Power | KW | 1.5 | 2.2 | 3 | 7.5 | 11 | 15 | |
| Motor Power | KW | 7.2 | 9 | 10.8 | 33.75 | 45 | 45 | |



Certificate
Radiant Tubes,Pex Tubing For Radiant Heat,Radiant Tube Heater,Radiant Pipe
Jiangsu Kinuo Furnace Roller Co., Ltd. , https://www.jskinuoroller.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)