Carbon and sulfur are important elements in determining the specifications and quality of steel products. Carbon with a content of more than 1.70% is called cast iron and less than 1.70% is called steel. Generally , the steel with a carbon content higher than 0.60% is called high-carbon steel. The steel with a carbon content between 0.25% and 0.60% is called medium-carbon steel. The steel with carbon content less than 0.25% is called low-carbon steel and the carbon content is less than 0.04% . Called industrial pure iron.
Carbon plays an important role in the performance of steel : As the carbon content increases, the hardness and strength of the steel increase, and the toughness and plasticity decrease. On the contrary, when the carbon content decreases, the hardness and strength decrease, and the toughness and plasticity increase. Carbon-sulfur analyzer is a commonly used measuring instrument in the physics and chemistry analysis room of an enterprise. It is used to quantitatively analyze the contents of carbon and sulfur in metal and non-metal materials, and is widely used in metallurgy, casting, machinery, vehicles, and valves. Ore, environmental protection, quality inspection and other industries and fields, can be quickly and easily carried out raw material acceptance, furnace analysis, product testing and other stages of analysis and testing.
Sulfur exists in steel and deteriorates the quality of the steel, reducing its mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and weldability. In particular, sulfur in steel, if it exists in the state of iron sulfide, due to its melting ( about 1000 °C), will cause the phenomenon of " hot brittleness " of the steel , that is, thermal deformation, cracks at high temperature work, affect the quality of the product And service life. Therefore, the lower the sulfur content in the steel, the better. In general requirements, the sulfur content in ordinary steel is less than 0.050%, the sulfur content in tool steel is less than 0.045% , and the sulfur content in high-quality steel is less than 0.020% .
In view of the important role of carbon and sulfur content in the quality and performance of steel, it is of great significance to examine the carbon and sulfur content in steel, that is, carbon and sulfur analysis.
The carbon and sulfur elements in the iron and steel are combusted at high temperatures ( 1200 °C to 1400 °C). All of them can be converted into gases to generate CO2 and SO2 . This is the basis for the combustion analysis of carbon and sulfur.
The principle of carbon-sulfur analysis is to pass the sample in a high-temperature furnace (such as a resistance furnace, also called a tubular furnace, an electric arc furnace, a high-frequency induction combustion furnace, etc.) through oxygen combustion to generate and release CO2 and SO2 gases. The separation of carbon and sulphur from metal elements and their compounds is measured, then the content of CO2 and SO2 is determined and the content of carbon and sulphur in the sample is converted. The general measurement methods are the following:
1. Infrared spectrophotometry: The carbon and sulfur in the sample are heated at high temperatures under oxygen-enriched conditions and oxidized to carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide gas. After the gas is processed into the corresponding absorption tank, the corresponding infrared radiation is absorbed and transmitted by the detector as a signal, and the output is processed by a computer. This method has the characteristics of accuracy, rapidity, and high sensitivity. Both the high and low carbon and sulfur content are used. The infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer using this method has a higher degree of automation and higher prices, and is suitable for applications where the analytical accuracy is high.
2. Volumetric method: Commonly used carbon measuring methods are gas volumetric method and non-aqueous titration method. Sulfur measurement is iodometric method and acid-base titration method. In particular, the gas volumetric method for the determination of carbon and iodine content is a fast and accurate method. It is the most common method for the combined determination of carbon and sulfur in China. The precision of carbon and sulfur analyzers using this method has a lower limit of carbon content of 0.050% and sulfur content. The lower limit is 0.005% , which can meet the needs of most occasions.
3. Gravimetric method: Alkali asbestos is used to absorb carbon dioxide, and the carbon content is determined by " incremental " . Determination of sulfur commonly used wet method, the sample with acid decomposition oxidation, converted to sulfate, and then in the hydrochloric acid medium was added cesium chloride, barium sulfate generated by precipitation, filtration, washing, burning, weighing the final calculation of sulfur The content. The disadvantage of the gravimetric method is that the analysis speed is slow, so it is not possible to use the carbon and sulfur analysis at the enterprise site. The advantage is that it has a high degree of accuracy. It is still recommended as a standard method at home and abroad and is applicable to standard laboratories and research institutes.
4. Conductivity method: Conductivity method for the determination of carbon and sulfur, which is characterized by accuracy, speed, and sensitivity. Mostly used for low carbon, low sulfur determination.
5. Determination of carbon and sulfur content in metals, as well as ICP , direct reading spectrometry, X- ray fluorescence, mass spectrometry, chromatography, activation analysis, etc., have their own advantages and scope of application.
At present, there are mainly the following types of carbon-sulfur analyzers used in China:
Infrared carbon-sulfur analyzer , high-speed carbon-sulfur analyzer, non-aqueous carbon-sulfur analyzer. Nanjing Ningbo Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd. is producing several types of carbon sulfur analyzers. Users can choose according to their own needs and the advantages and disadvantages of various types of carbon and sulfur analyzers.
Nanjing Ningbo Analysis Instrument Co., Ltd.
2016.10.10
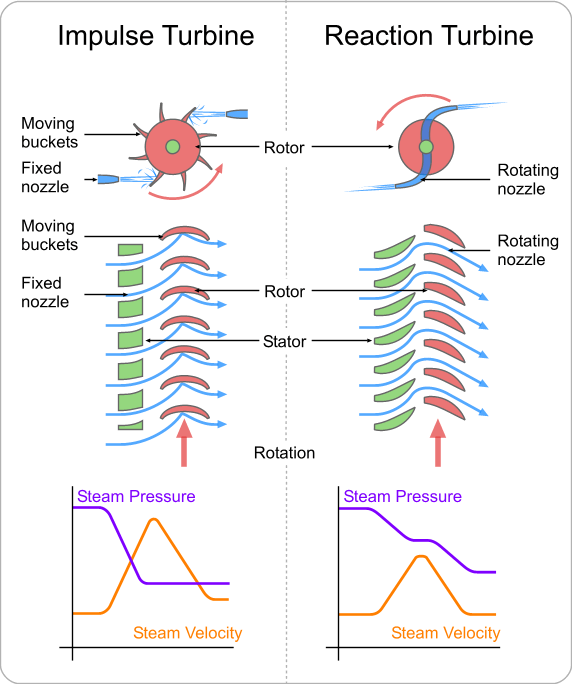
A reaction turbine is a type of Steam Turbine that works on the principle that the rotor spins, as the name suggests, from a reaction force rather than an impact or impulse force.
In a reaction turbine there are no nozzles to direct the steam like in the impulse turbine.
Instead, the blades that project radially from the outer edge of the rotor are shaped and mounted so that the shape between the blades, created by the cross-section, create the shape of a nozzle. These blades are mounted on the revolving part of the rotor and are called the moving blades.
The fixed blades, which are the same shape as the moving blades, are mounted to the outer casing where the rotor revolves and are set to guide the steam into the moving blades. Below is a simple diagram of reaction turbine blades:
Reaction Turbine Principle:
In the case of reaction turbine, the moving blades of a turbine are shaped in such a way that the steam expands and drops in pressure as it passes through them. As a result of pressure decrease in the moving blade, a reaction force will be produced. This force will make the blades to rotate.
Reaction Turbine Working:
A reaction turbine has rows of fixed blades alternating with rows of moving blades. The steam expands first in the stationary or fixed blades where it gains some velocity as it drops in pressure. Then enters the moving blades where its direction of flow is changed thus producing an impulse force on the moving blades. In addition, however, the steam upon passing through the moving blades, again expands and further drops in pressure giving a reaction force to the blades.
This sequence is repeated as the steam passes through additional rows of fixed and moving blades.
Note that the steam pressure drops across both the fixed and the moving blades while the absolute velocity rises in the fixed blades and drops in the moving blades.
The distinguishing feature of the reaction turbine is the fact that the pressure does drop across the moving blades. In other words, there is a pressure difference between the inlet to the moving blades and the outlet from the moving blades.
Special Aspects of Reaction Turbines
- There is a difference in pressure across the moving blades. The steam will, therefore, tend to leak around the periphery of the blades instead of passing through them. Hence the blade clearances as to maintain as minimum as possible.
- Also, due to the pressure drop across the moving blades, an unbalanced thrust will be developed upon the rotor and some arrangement must be made to balance this.
Reaction Steam Turbine
Shandong Qingneng Power Co., Ltd. , https://www.qnpturbines.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)